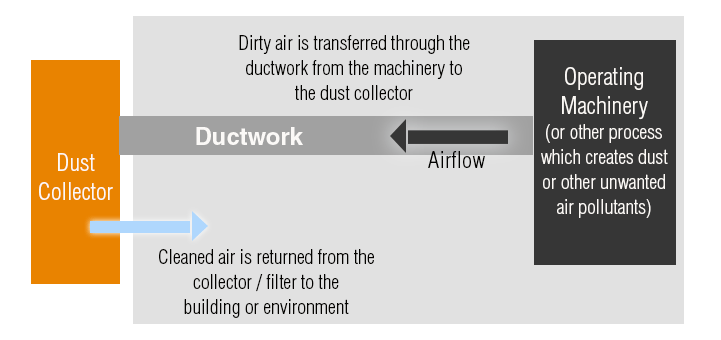
Industrial ventilation / dust collection, sometimes known as Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV), is the process of moving clean air into a work environment and exhausting contaminated air out. In its simplest form, an industrial ventilation or dust collection system can be described as similar to a vacuum cleaner. The dust collection ductwork is the hose and wand that draws the dust away from the machine creating pollutants. And the dust collector is the vacuum cleaner filtering dust and returning clean air either to the building or outside.
 Flexible Hose is a rubber or plastic hose with a metal grounding helix that MUST be grounded at each end to keep static electricity from building up and generating dangerous sparks. Hose is only appropriate for short runs, such as machine connections. That is because its rough interior and “floppy” nature cause significant static pressure loss, which requires higher energy use and can result in poor system performance.
Flexible Hose is a rubber or plastic hose with a metal grounding helix that MUST be grounded at each end to keep static electricity from building up and generating dangerous sparks. Hose is only appropriate for short runs, such as machine connections. That is because its rough interior and “floppy” nature cause significant static pressure loss, which requires higher energy use and can result in poor system performance.Hard, Fixed Dust Collection Ductwork is most often constructed out of either plastic or metal (galvanized or stainless steel, depending on the application). All-metal construction is used on virtually all industrial and commercial applications as it reduces the chance of dangerous static electricity buildup. The smooth rigid interior of metal duct reduces static pressure loss, even over long runs. Metal duct construction types could include spiral wound or seamed.
 Flanged ducting is joined using metal flanges or angle rings. In this method, flanges are fitted over each end of the duct collar and the edge of the duct is “vanstoned” (turned up to keep the flange in place) or the flange can be welded to the duct. Then the flanges on the ends of two pieces of duct are simply bolted together to join pieces.
Flanged ducting is joined using metal flanges or angle rings. In this method, flanges are fitted over each end of the duct collar and the edge of the duct is “vanstoned” (turned up to keep the flange in place) or the flange can be welded to the duct. Then the flanges on the ends of two pieces of duct are simply bolted together to join pieces. Clamp-Together ductwork systems, such as Nordfab® Quick-Fit®, in which each section of duct has a rolled edge that is joined quickly with a simple tool-free clamp, offer many advantages, including:
Clamp-Together ductwork systems, such as Nordfab® Quick-Fit®, in which each section of duct has a rolled edge that is joined quickly with a simple tool-free clamp, offer many advantages, including:Nordfab is the originator and world's largest manufacturer of clamp-together ductwork.
Dust collection ducting is sometimes referred to as blow pipe.
 Above: Nordfab® Quick-Fit and flanged ductwork installed in an industrial manufacturing facility's dust collection system
Above: Nordfab® Quick-Fit and flanged ductwork installed in an industrial manufacturing facility's dust collection system
| Want to learn more about Combustible Dust Design? |
|---|
| Nordfab Ducting co-sponsored the Overlooked Aspects of Combustible Dust Design webinar presented by Powder & Bulk Solids magazine on January 25, 2023. It is not too late to learn from this educational webinar which is now available in a recording. |
|
Click here to learn more about the webinar and get a link to view the recording
|
